Latest News
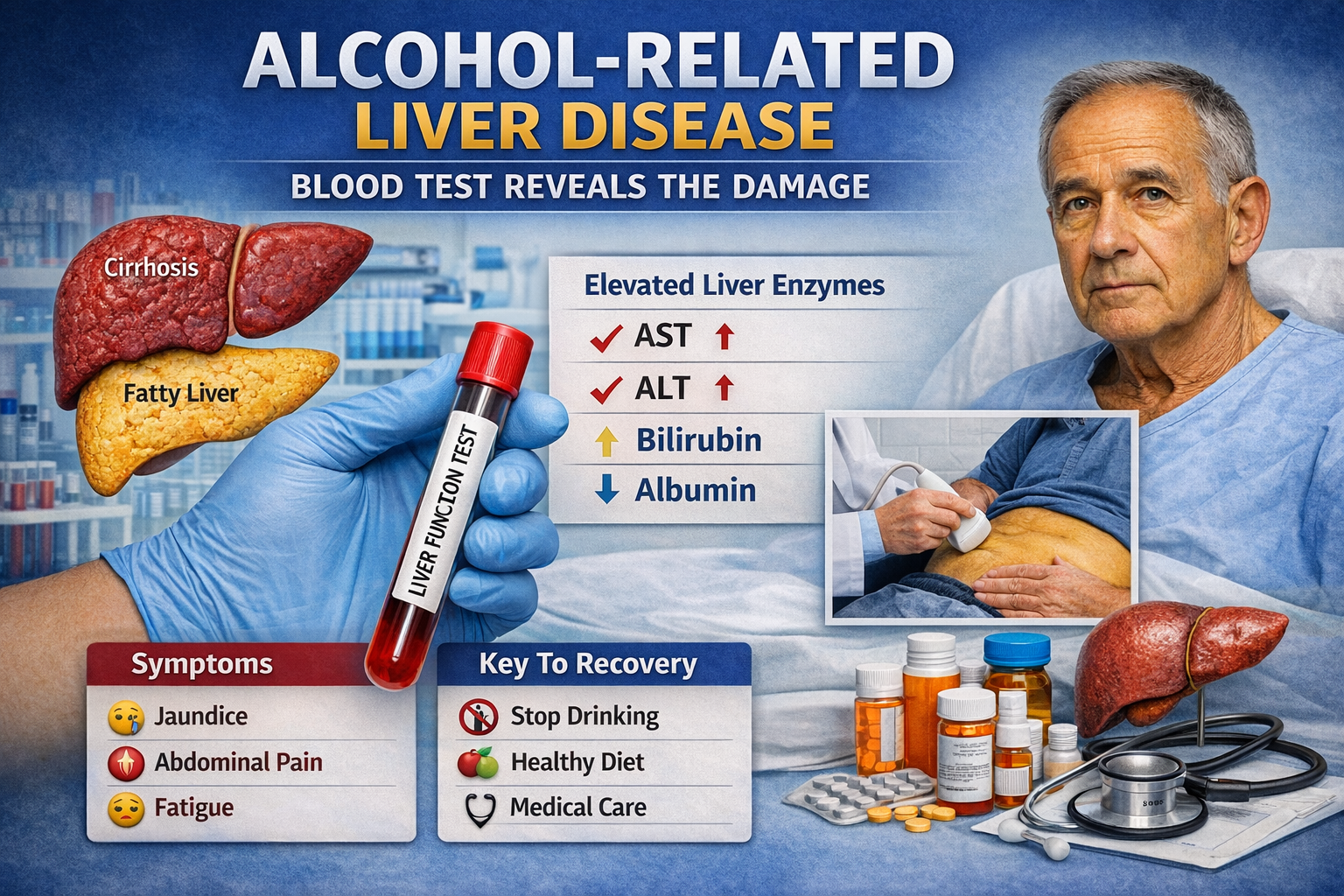
Blood Test Reveals Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
Alcohol-Alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD) is a serious health condition caused by excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption. The liver plays a vital role in filtering toxins from the blood, producing proteins, and…

Telemedicine Visits Cost Five Times Less Than In-Clinic Care
Clinic-Telemedicine has transformed the healthcare landscape by making medical consultations more accessible, convenient, and affordable. In recent years, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, virtual healthcare visits…
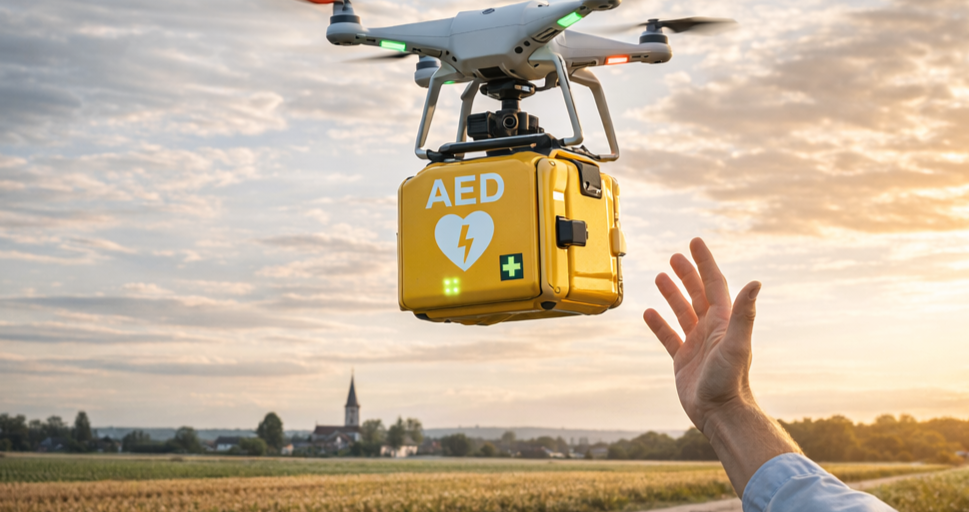

Could Drone-Delivered Defibrillators Save Lives?
Drone-Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. It occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating effectively, cutting off blood flow to the brain and other vital organs. Survival…
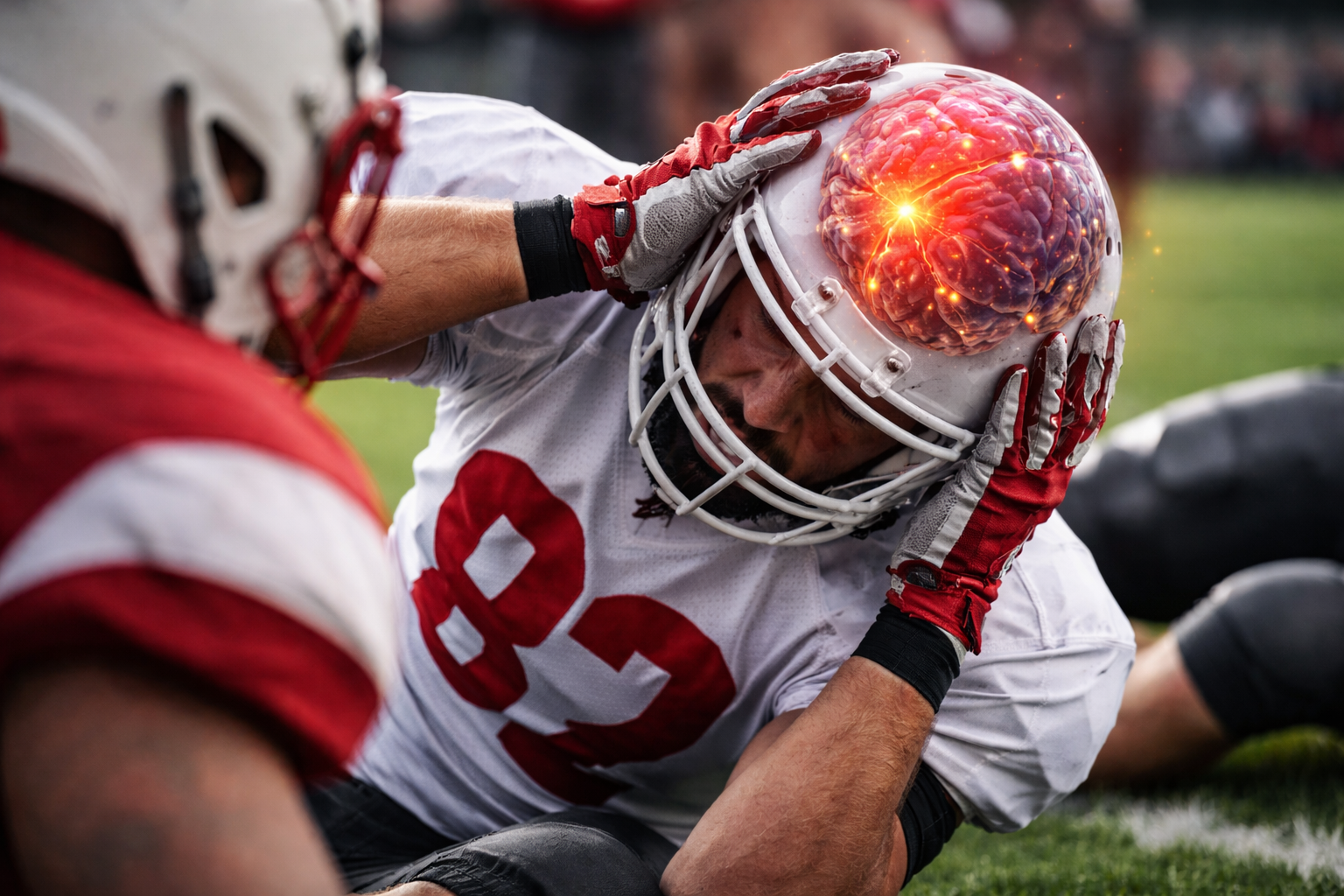

Inflammation Linked To Brain Damage, Memory Problems Among Football Players
Football-Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. It occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating effectively, cutting off blood flow to the brain and other vital organs. Survival…
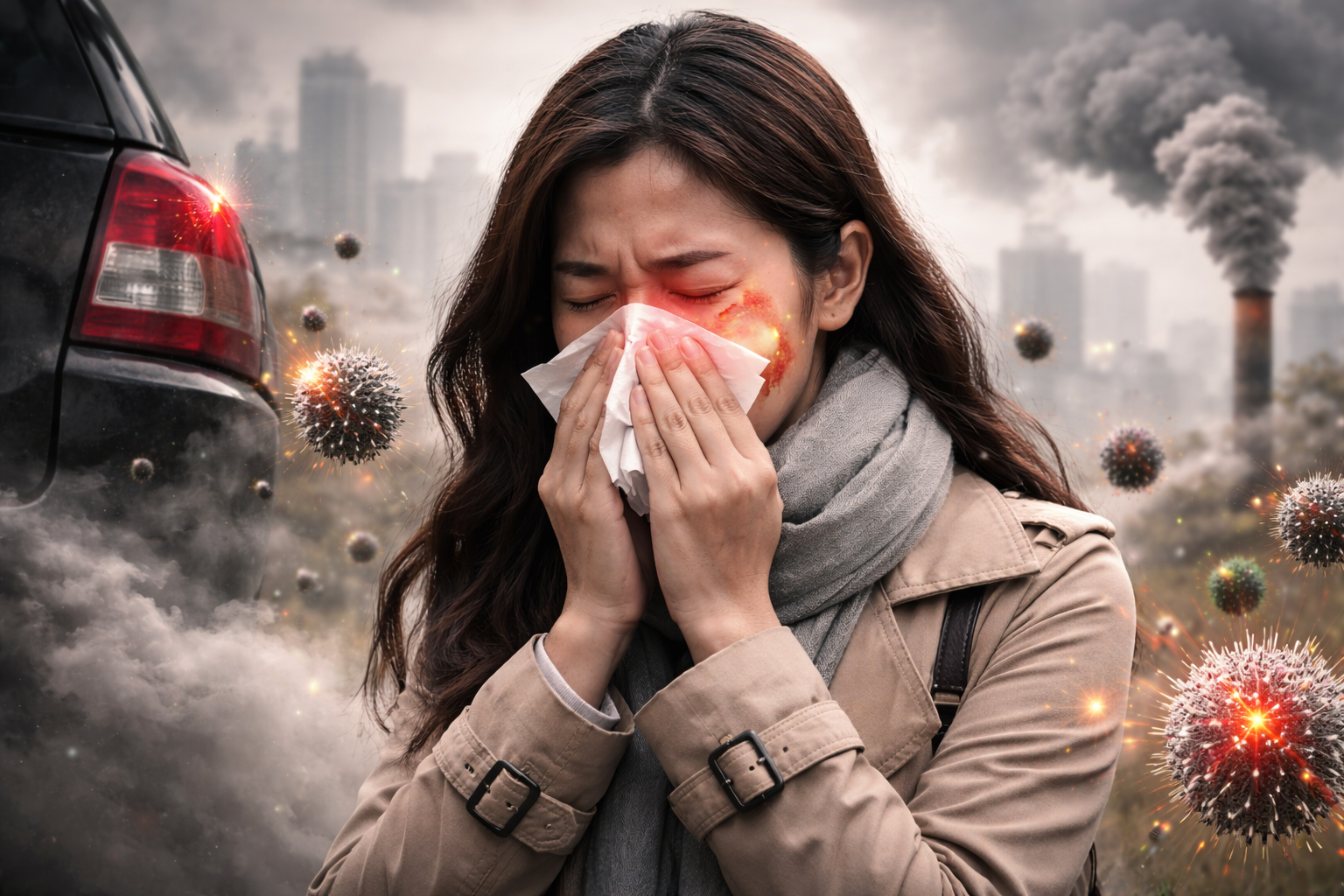

Causal Link Identified for Air Pollution and Outpatient Visits for Chronic Rhinitis
Pollution-Emerging research has identified a causal relationship between air pollution exposure and increased outpatient visits for chronic rhinitis. Chronic rhinitis, characterized by persistent nasal inflammation,…

Higher Tumor Burden Seen for Male Patients With Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma
Tumor -Multiple myeloma is a cancer of plasma cells that primarily affects the bone marrow and disrupts the production of normal blood cells. Recent clinical observations and studies indicate that male patients….

Laughing, Crying Are Normal But Rare Responses To Orgasm, Women & Study Reveals
Laughing – Orgasm is often understood as a physical and emotional release associated with sexual pleasure. However, a recent study highlights that some women experience unexpected emotional responses—such as laughing or crying—during orgasm….

Your Teen Sleeping In During The Weekend? It Could Protect Them From Depression, Experts Say
Sleep -Teenagers often face early school start times, heavy homework loads, and social commitments that can disrupt their natural sleep patterns. Recent research suggests that allowing teens to sleep in during weekends may help…
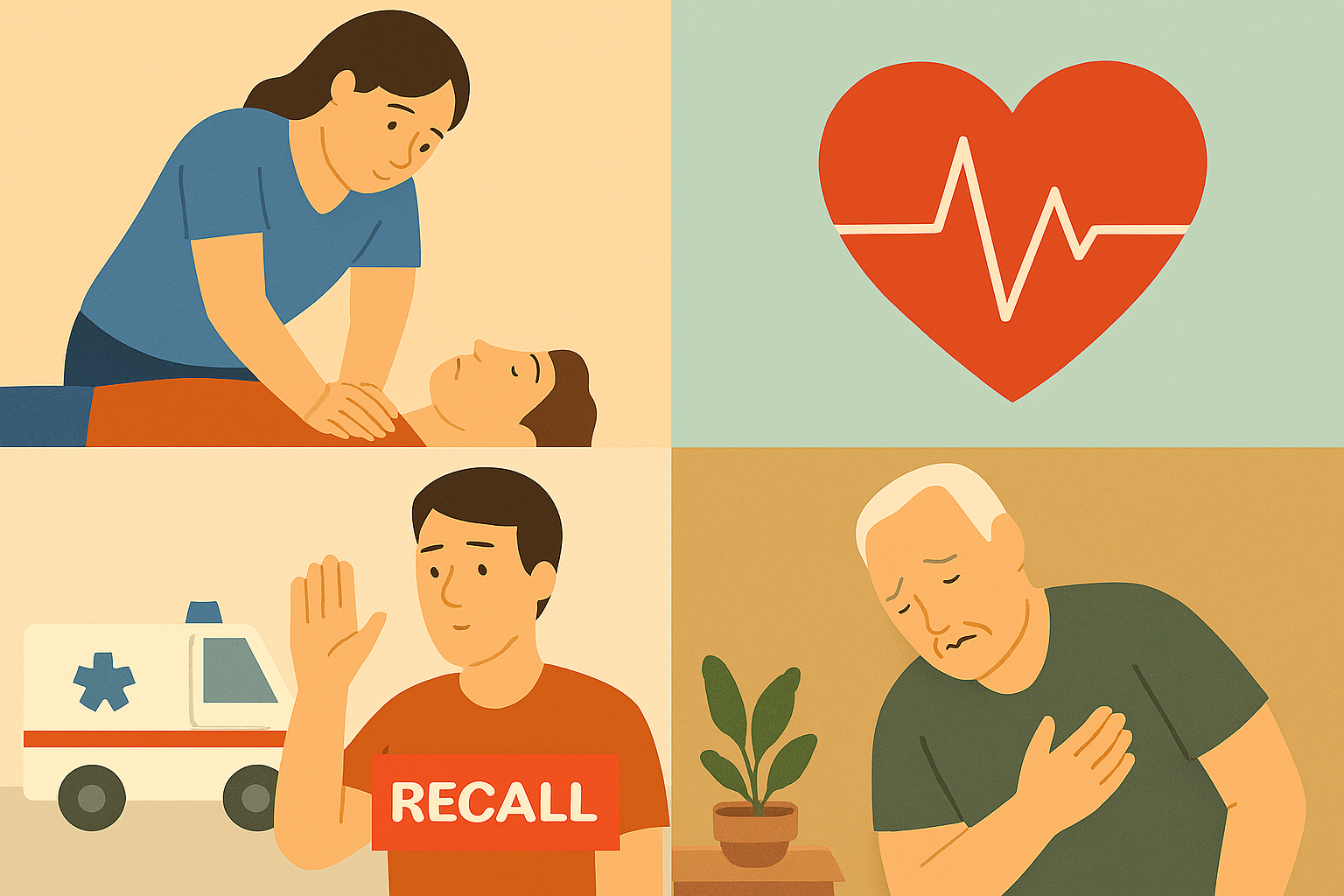

What Is CPR and Who Needs It?
CPR-Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a life-saving emergency procedure used when a person’s breathing or heartbeat has stopped. This can happen due to cardiac arrest, drowning, severe injury, choking, or other….

Poll Shows Most Americans Want to Slim Down
Slim -Recent polls and health surveys reveal a clear trend across the United States: most Americans want to slim down. This growing desire reflects increasing awareness about health, fitness, and lifestyle-related diseases…..

Tamales Sold in California, Nevada Recalled Over Listeria Risk
Risk – A recent recall of tamales sold in California and Nevada has raised public health concerns due to the potential risk of Listeria monocytogenes contamination. Food recalls like this are issued to protect consumers..

Weight Often Returns After Stopping Ozempic, Wegovy, Study Finds
Weight-Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a long-term condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Patients with CKD experience a wide range of symptoms such as fatigue, itching, sleep problems, pain, nausea, and difficulty concentrating….
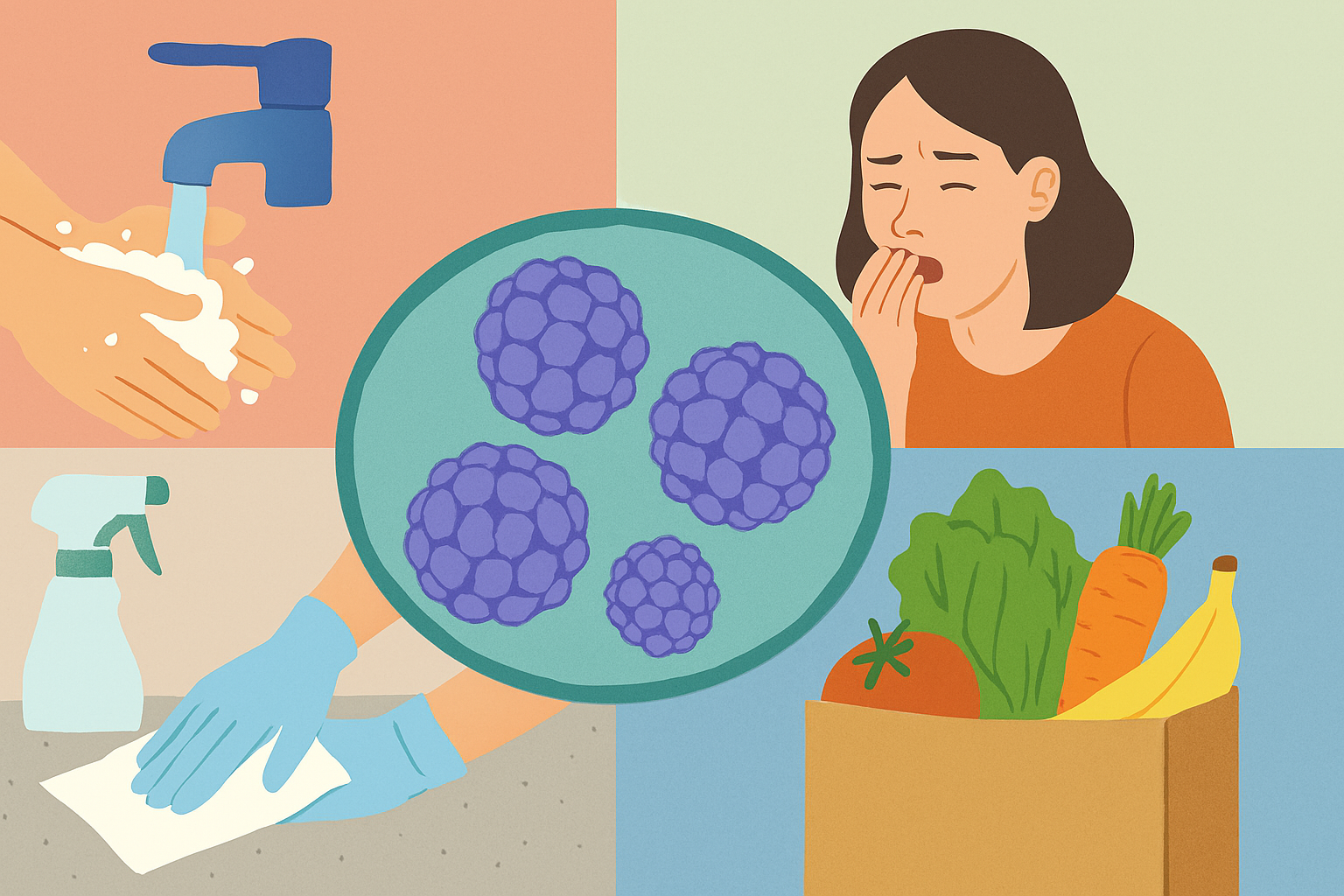

What You Need to Know to Prevent And Fight Norovirus
Norovirus-Norovirus is a highly contagious virus and one of the leading causes of acute gastroenteritis worldwide. It affects people of all ages and spreads rapidly in communities, schools, healthcare facilities, cruise ships, and households. The virus causes ….
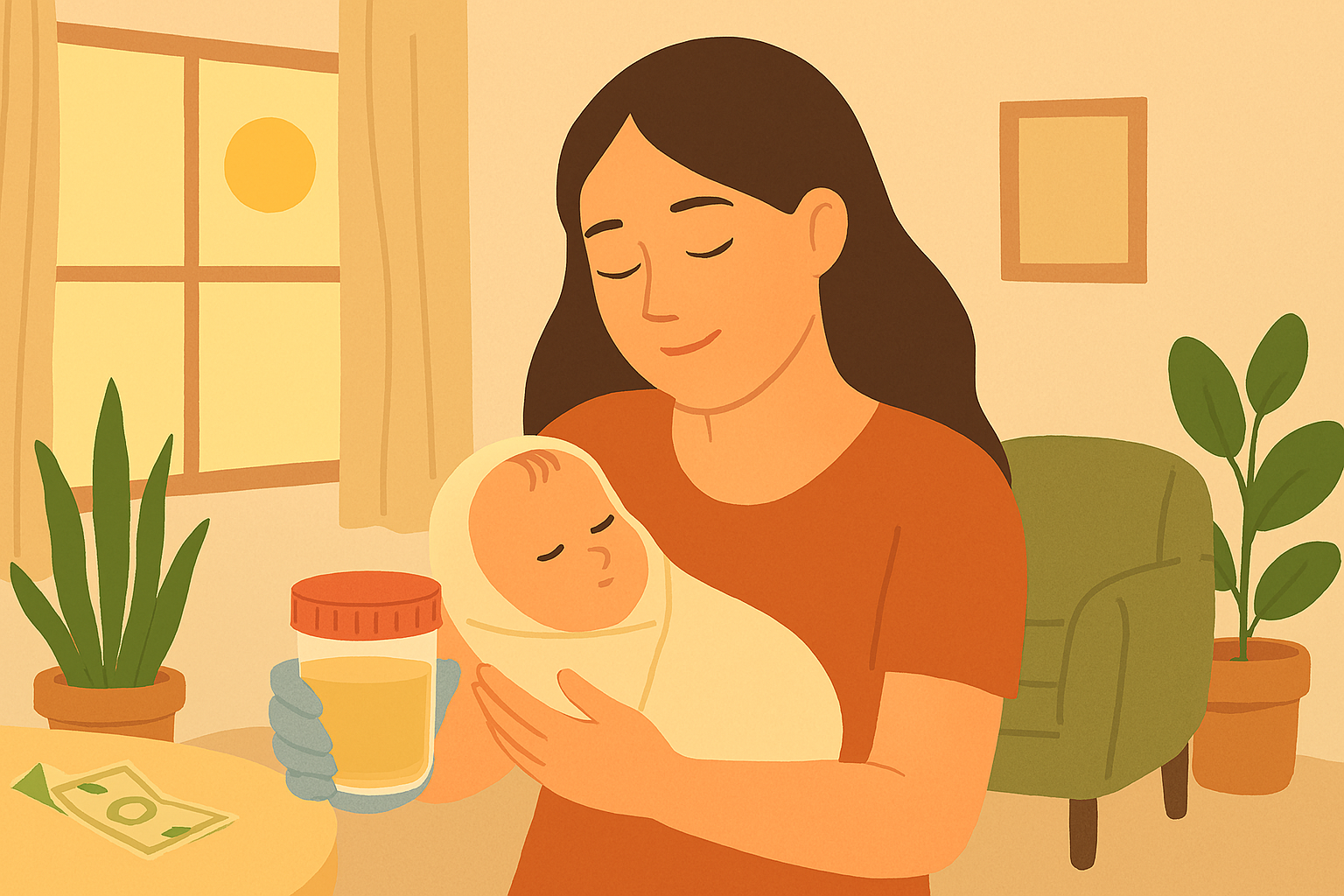

Breastfeeding Linked to Lower Odds of Depression, Anxiety
Breastfeeding – Breastfeeding is widely recognized for its physical health benefits for infants, including improved immunity and nutrition. In recent years, growing research has also highlighted its positive impact on maternal mental..

Guidance Updated for Laboratory Testing for Drugs of Misuse in ED
Drugs -Laboratory testing for drugs of misuse plays a critical role in emergency department (ED) care. Updated guidance reflects advances in testing technology, evolving patterns of substance use, and the need for..
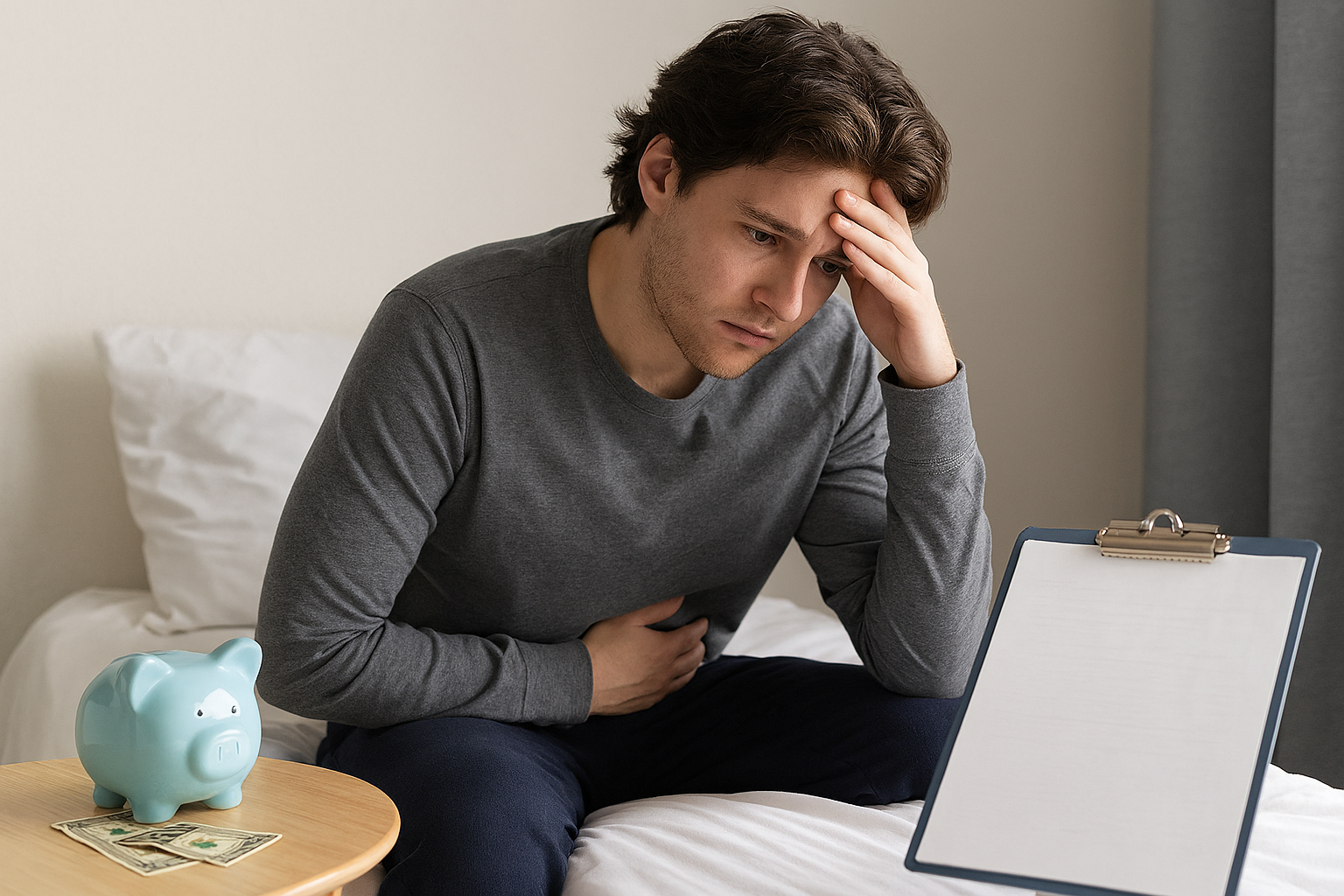

Young Adults With IBD Face Health Care Access Challenges, Financial Burden
Adults-Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is a chronic condition that often begins in adolescence or early adulthood. Young adults living with IBD must manage lifelong symptoms such as abdominal pain,
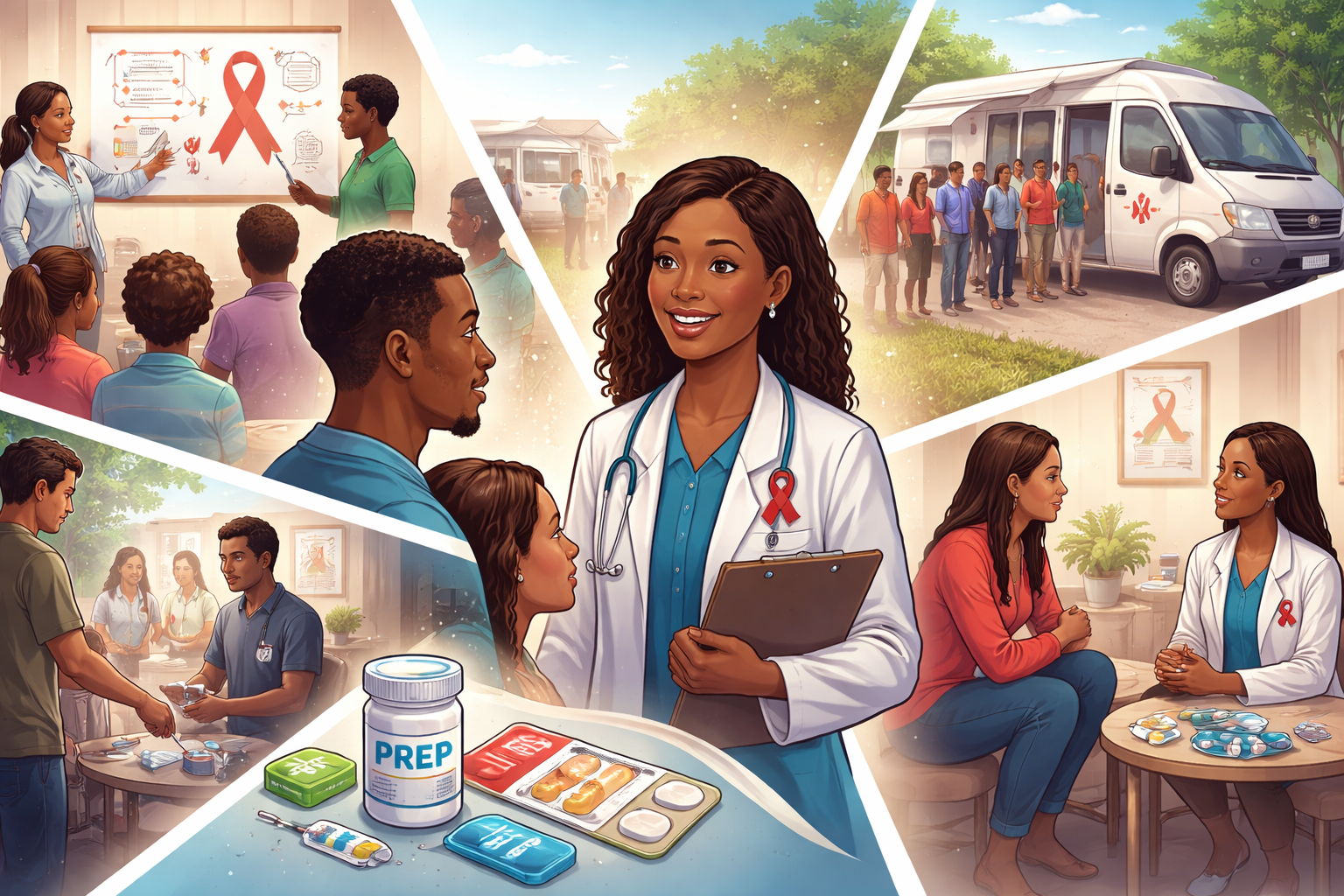

Overcoming Obstacles to HIV Prevention
HIV-Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a long-term condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Patients with CKD experience a wide range of symptoms such as fatigue, itching, sleep problems, pain, nausea, and difficulty concentrating….
HIV Viral Load Test With Next-Day Results Does Not Impact Linkage to Care
HIV-Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a long-term condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Patients with CKD experience a wide range of symptoms such as fatigue, itching, sleep problems, pain, nausea, and difficulty concentrating….

